A co-operative bank is a small-sized establishment that is established under the Co-operative Societies Act of the different states of India. These banks are established under different levels like the state level, district level, city level, village level, etc.
They are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and have a motive of “No Profit, No Loss”. It is because of this that they don’t look to maximize their profit.
In India, the co-operative banks are governed according to the Banking Regulations Act 1949 and Banking Laws (Co-operative Societies) Act, 1955. These banks play an important role in last-mile credit delivery and extend their financial services across the country.
Structure of Co-operative banks in India
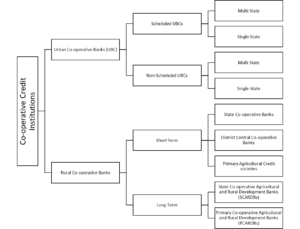
The Co-operative Banks in India can be divided into two broad categories. The first is the Urban Co-operative Banks (UCBs) and the second is Rural Co-operative Banks (RCBs). In India, there are 1853 UCBs and 1,09,924 BCBS. These UCBs and RCBs can be further divided into different categories.
The UCBs can be divided into Scheduled UCBs and Non-Scheduled UCBs. A Scheduled UCB is a banking corporation whose minimum paid-up capital is ₹5 lakh. These rules do not apply to a non-scheduled UCB. These Scheduled UCBs can be further divided into Multi-State UCBs and Single State UCBs. A multi-state UCB is a bank that has branches in more than one state. A Single state UCB only has branches in its specific state.
In India, there are only 24 multi-state UCBs while 31 single-state UCBs. The non-scheduled on the other hand can also be divided on the basis of how many states it has branches in. Only 10 Non-Scheduled UCBs in India are multi-state UCBs while there are 1,788 Non-Scheduled UCBs that have only a single branch in one city or a few branches within the state itself.
The RCBs can be divided into two parts as well. These parts are named to be Short Term RCBs and Long Term RCBs. The Short-Term RCBs can be divided into three different parts. Namely, the State Co-operative Banks, which work within an entire state, District Central Co-operative Banks which are restricted within a District, and the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies, which are only limited within the boundaries of a village.
The Long Term RCBs can be divided into SCARDBs and PCARDBs. The SCARBDs stands for State Co-operative Agricultural and Rural Development Banks. These banks although belonging to the Rural Population have access to many different states. PCARDBs on the other hand stand for Primary Co-operative Agricultural and Rural Development Banks.
Features of Co-operative banks
- Customer Owned Entities
- One person, one vote
- Financial Inclusion
- Part of the yearly profit of the bank is distributed among the co-operative members of the bank
- Farmer loans at minimum interest
- Easy and accessible loans and credit benefits in rural areas
Advantages of Co-operative banks
- Aid provision in rural areas
- Lower interest rates in villages in comparison to local money loaners
- Greater reach
- Believe in mutual help
- High interest on deposits and low interest on loans
- Promote productivity
- Provide agricultural credits to farmers
- Encourages savings and investments
- Discourages unproductive borrowing
Disadvantages of Co-operative Banks
- Needs of tenants not fully met
- Tough to find investors
- The benefits are enjoyed by the rich instead of helping the poor
- Not equally developed across the country
- Have political interference
- Large overdue
- Long term extension is denied
Top 5 Co-operative Banks in India
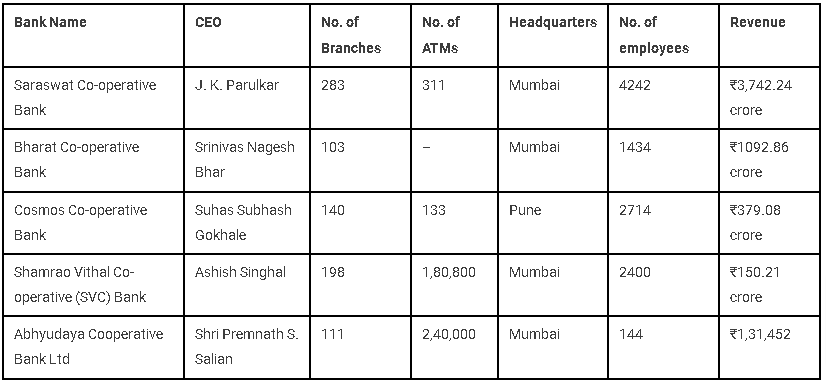
1. Saraswat Co-operative Bank
Customer Care Number: 1800 229 9999
The Saraswat Co-operative Bank was founded in the year 1918, in the city of Mumbai. This bank has its branches in six states and has a gross profit of over ₹650 crores. The Saraswat bank has also won the “Best Technology Bank of the Year” award in 2019. As Saraswat bank provides different facilities to its customers. Sarawat Bank’s 3-in-1 Account helps you manage all three—Savings, Demat, and Trading with zero problems. It lets you invest and trade through a mobile app, computer, or phone call.
2. Bharat Co-operative Bank
Customer Care Number: 022 6189 0091
The bank was founded in the year 1978. The bank has an approximate customer base of 5.5 lakh in India and has won the “Best Urban Cooperative Bank” award in 2017 and the “Best Information Technology” award in the year 2016.
3. Cosmos Co-operative Bank
Customer Care Number: 020 6708 6708
The bank is traced to being founded in the year 1906. It is the first bank in India to open a currency chest with the permission of RBI. The main value that the bank follows is “TRUST” and because of this, the bank has flourished.
4. Shamrao Vithal Co-operative (SVC) Bank
Customer Care Number: 1800 313 2120
This bank is spread across ten states in India and has been founded in the year 1906. The bank has been awarded the “Best Urban Cooperative Bank” award in 2018 by the Brihan Mumbai Nagari Sahakari Banks Association.
5. Abhyudaya Cooperative Bank Ltd
Customer Care Number: 022 6877 8900
Despite the fact that this bank was founded after independence i.e. in 1964, it has still managed to make its place in the Top 5. The Abhyudaya Cooperative Bank has 111 branches in the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Gujarat. The other branches are scattered in other states. The bank has won the “Best IT Enabled Cooperative Bank” in the year 2014-15.




