Discover
-
The key steps for salaried individuals to file their Income Tax Return online
-
Different types of Income Tax Return forms applicable to salaried individuals and their respective criteria
-
What are some commonly overlooked tax exemptions available to salaried employees under the Income Tax Act?
The Income Tax Act of 1961 mandates Indian taxpayers to pay Income Tax Returns on a timely basis. Filing an ITR is considered the moral and social responsibility of every responsible citizen of India.
Filing an ITR holds pivotal importance for every salaried individual as the tax returns act as proof of income, which helps in getting access to various financial products like loans. Moreover, a salaried person should file an ITR to avail of other benefits like claiming tax refunds, quick visa processing, adjustment of capital gains or losses etc.
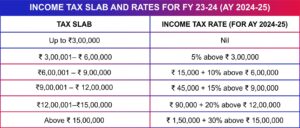
Let’s first take a look at income tax slab rates for the Financial Year 2023-24 for Salaried employees:
INCOME TAX SLAB AND RATES FOR FY 23-24 (AY 2024-25)
| Tax Slab | Income Tax Rate (For AY 2024-25) |
| Up to ₹3,00,000 | Nil |
| ₹ 3,00,001– ₹ 6,00,000 | 5% above ₹ 3,00,000 |
| ₹6,00,001 – ₹ 9,00,000 | ₹ 15,000 + 10% above ₹ 6,00,000 |
| ₹9,00,001 – ₹ 12,00,000 | ₹ 45,000 + 15% above ₹ 9,00,000 |
| ₹12,00,001–₹15,00,000 | ₹ 90,000 + 20% above ₹ 12,00,000 |
| Above ₹ 15,00,000 | ₹ 1,50,000 + 30% above ₹ 15,00,000 |
There are some key documents that you need to be equipped with to file your correct income tax return. Some important ones are salary slips, form 10E, Form 16 from the employer, Foreign slips and other important documents.
Read: Essential Documents required to file an ITR
ITR APPLICABLE FOR SALARIED INDIVIDUALS
ITR-1 (SAHAJ) applicable for Individual
- Employees with a total income of up to Rs. 50 lakhs
- The total income includes earnings under the ‘Income from other sources’ alongside salaries
- Should not have more than one house property if you are filing ITR-1
- The income from agriculture should not exceed Rs. 5,000
ITR-2 Applicable for Individual and HUF
- If total income exceeds Rs. 50 lakhs
- Possesses more than one house property
- Generate income from capital gains and/or other sources, but not from profits from any business
ITR-3 Applicable for Individual and HUF
- Every income from ITR 2
- If you receive income from business
- If you are a partner in a firm
ITR-4 (SUGAM) – Applicable for Individual, HUF and Firm (other than LLP)
- Individuals or Hindu Undivided Families (HUF) who are residents but not ordinarily residents, or firms (excluding LLPs)
- Every income from ITR 1
- Presumptive income (under sections 44AD, 44ADA, or 44AE)
- Income from sources including salary/pension, one house property
- Other sources like interest, family pension, dividends, etc
HOW TO FILE AN ITR ONLINE FOR SALARIED EMPLOYEES?
Step 1: Login on Portal
- Open the e-filing portal of the Income Tax Department
- Click on ‘Login’
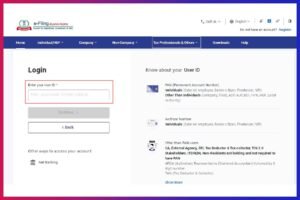
- Enter your user ID
- Click on ‘Continue’
- Check the security message in the tick box
- Enter the ‘Password’
- Click on ‘Continue’
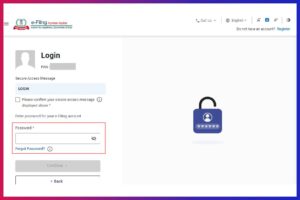
If you haven’t registered, sign up using your PAN Number, which will then serve as the User ID.
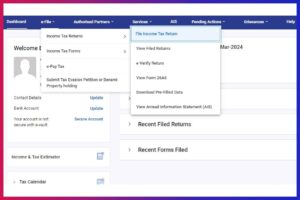
Step 2: File Income Tax Return
- At the top of the page, find the ‘e-File’ option
- Click on ‘Income Tax Returns’
- Click on ‘File Income Tax Return’
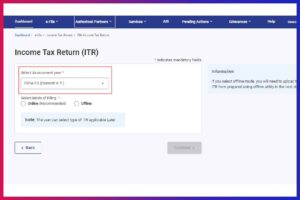
Step 3: Select the Assessment year
- Select the ‘Assessment Year’ as “2024-25 (Current A.Y.)”
- If you are filing returns for FY 2022-23, select “2023-24”
- Select Mode of Filing as ‘Online’
- Click on ‘Continue’
Step 4: Select ‘Status’
- If you are filing for individual, click on ‘Individual’ and then click on ‘Continue’
Step 5: ITR Form
- You need to select which ITR form you need to file. (Check the information given above about ITRs)
- Once you select the ITR form, click on ‘Proceed with ITR ‘X’ (x denotes ITR Form type)’
- Click on ‘Let’s Get Started’
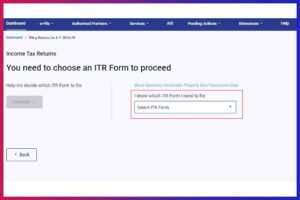
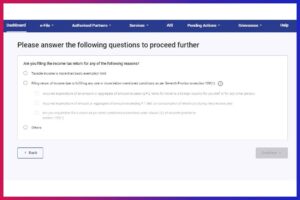
Step 6: Answer The Questions
- In this step, you need to answer some questions to proceed further (reason for filing ITR):
- Taxable income is more than the basic exemption limit
- Filing return of income due to fulfilling any one or more below-mentioned conditions as per Seventh Proviso to section 139(1):
- Others
- Select the appropriate option and ‘Continue’
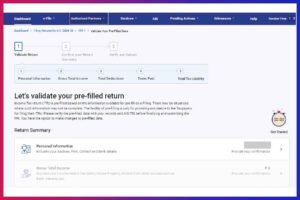
Step 7: Verify the Pre-filled information
- Take a look at the pre-filled information including your Personal information like Aadhar, Date of Birth, Bank Details, Address, and Contact details.
- Click on ‘Confirm’
- Enter your ‘Gross Total Income’, ‘Total Deductions’, ‘Tax Paid’ and ‘Total Tax Liability’
- Confirm the summary of your tax return, verify the details, and make payment for any remaining taxes owed, if applicable.
Step 8: ITR Verification
Validate your income tax return by generating an Electronic Verification Code (EVC) or a One Time Password (OTP) through one of the following methods:
- Generate EVC using your bank’s ATM
- Generate OTP through your Aadhaar Card
- Use a pre-validated bank account
- Use a pre-validated Demat account

If you choose not to e-verify on your own, you can send a physical copy of your ITR form to CPC Bengaluru. The address is mentioned in the form.
Step 9: Submit ITR
Click on ‘Submit’ to successfully submit your ITR.
You will receive an acknowledgement on your email address.
It’s done!
Read the consequences of not filing an ITR here: What happens if you don’t file an Income Tax Return?
TAX EXEMPTIONS FOR SALARIED EMPLOYEES?
Salaried employees can avail tax exemptions under Section 80C, 80CCC, 80CCD (1), 80D, 80E, 80G, and 80TTA.
Section 80C, 80CCC, 80CCD (1)
Section 80C is most commonly used for saving income tax. An individual can claim deductions up to Rs. 1.5 lakh for a tax deduction for those who invest or spend on stipulated tax-saving avenues. Some investments that are eligible for an exemption under Section 80C, 80CCC, 80CCD (1) up to a maximum of Rs. 1.5 lakh are-
- Life insurance premium
- Equity Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS)
- Fixed Deposit (Tax Savings)
- Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
- Annuity/ Pension Schemes
- Tuition fees for children
- Principal payment on home loans
- Sukanya Samriddhi Account
- NSC (National Saving Certificate)
- Post office time deposits
- Contribution to PPF Account
- National Pension Scheme
Section 80D
Section 80D is a deduction that an individual claims on medical expenses. One can save tax on medical insurance premiums paid for the health of self, dependent parents, and family.
The limit for Section 80D deductions is-
- Rs. 25,000 for premiums paid for self/family members.
- Rs. 50,000 for premiums paid for senior citizen parents.
- Health checkups to the extent of Rs. 5,000 are covered additionally within the overall limit.
- Deduction up to Rs. 50,000 to medical expenditure incurred by the senior citizen (60 years or above) or towards senior citizen parents (provided, not covered under mediclaim policy).
Section 80E
This section includes a deduction of interest paid on loans taken for pursuing higher education from taxable income. To elaborate, an education loan taken on behalf of children, spouse, or student for whom the taxpayer is the legal guardian is applicable for deduction under this section.
Section 80G
One can claim contributions made to charitable organizations, and relief funds as a deduction under Section 80G of the IT Act. However, it does not include all donations. Only donations made to prescribed funds qualify as a deduction.
Section 80TTA
This section offers a deduction of up to Rs. 10,000 on income earned from savings account interest. If the income from bank interest is less than Rs. 10,000, the whole amount is allowed as a deduction but if the amount exceeds, the amount after that would be taxable.
In conclusion
Filing your income taxes as a salaried person helps you prove your income and get access to things like loans. You can file your taxes online by logging into the income tax department website, filling out the proper details and submitting the form. Moreover, you might get some money back if you qualify for certain tax breaks.




